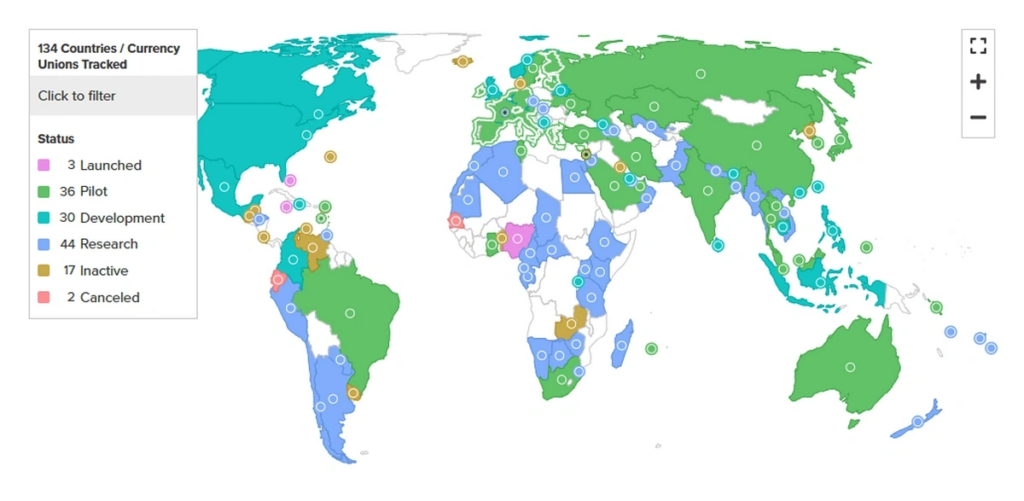
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are emerging as a hot topic in the financial world. With over 130 countries representing 98% of global GDP now developing or testing, the digital currency landscape is set to change dramatically.

CBDCs promise the benefits of cryptocurrencies without the volatility, offering a stable and secure digital payment system managed by central banks. Jamaica, Nigeria, and the Bahamas have already launched theirs, while China leads with its digital yuan pilot. As we look towards 2030, with predictions of more operational CBDCs, it’s crucial to understand their implications on both the traditional banking system and the cryptocurrency market.
Understanding CBDCs
A CBDC is a digital form of a country’s fiat currency issued and regulated by the central bank. Unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, which are decentralized, CBDCs are centralized, meaning they are controlled by the issuing authority. It aims to provide a secure, efficient, and inclusive payment system that can function alongside physical cash.
Global Developments and Key Players
Countries like Jamaica, Nigeria, and the Bahamas have already launched theirs. The Bahamas’ Sand Dollar was the first, introduced in 2020, aiming to improve financial inclusion and streamline payments. Nigeria’s eNaira, launched in 2021, targets similar goals, hoping to bring the unbanked population into the financial system and reduce transaction costs.
China’s digital yuan, known as e-CNY, is perhaps the most advanced and ambitious CBDC project to date. The People’s Bank of China (PBOC) has been working on this digital currency since 2014, and its pilot programs have been steadily expanding.
By 2023, e-CNY had processed over 100 billion yuan ($15.4 billion) in transactions. China’s goal is not only to modernize its financial system but also to reduce dependence on the U.S. dollar in international trade.
Advantages of CBDCs
Financial Inclusion: It provides banking services to the unbanked and underbanked populations. In developing countries, many people lack access to traditional banking systems. CBDCs can be accessed through mobile phones, making financial services more inclusive.
Efficiency and Cost Reduction: CBDCs can streamline payment systems, reduce transaction costs, and eliminate intermediaries. This can lead to faster and cheaper transactions compared to traditional banking.
Monetary Policy Implementation: It gives central banks a powerful tool to implement monetary policy more effectively. They can offer real-time data on money circulation and use, helping central banks make informed decisions.
Combatting Illegal Activities: Digital currencies can help reduce money laundering and other illegal activities by providing better transaction tracking and transparency.

Challenges and Concerns
While CBDCs offer numerous benefits, they also pose several challenges and concerns:
Privacy Issues: One of the main concerns is the potential loss of privacy. Unlike cash transactions, CBDC transactions can be tracked, raising concerns about surveillance and data security.
Technological Infrastructure: Implementing a CBDC requires robust technological infrastructure. Developing and maintaining this infrastructure can be costly and complex.
Cybersecurity Risks: It could become a target for cyberattacks. Ensuring the security of digital currency systems is paramount to prevent financial losses and maintain trust.
Impact on Traditional Banks: This could disrupt the traditional banking system. Banks might lose deposits as people switch to CBDCs, potentially affecting their ability to lend money.
Future Prospects
By 2030, the Bank of International Settlements predicts that 15 retail CBDCs (used by consumers and businesses) and 9 wholesale CBDCs (used by banks) will be operational. This development and adoption are expected to continue growing as central banks seek to modernize payment systems and enhance financial stability.
SWIFT, the global provider of secure financial messaging services, is planning to launch a network of CBDC platforms. This network aims to facilitate cross-border transactions, allowing different CBDCs to interoperate seamlessly. In tests conducted with 38 banks and financial platforms, SWIFT demonstrated the potential of this network to maintain efficiency and security in cross-border transactions.
Conclusion
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are emerging as a significant development in the global financial system. As of 2024, over 130 countries representing 98% of the world’s GDP are developing or testing their own CBDCs. This monumental shift promises to revolutionize how we think about money, combining the benefits of cryptocurrencies with the stability and oversight of traditional fiat currencies.
Visits: 9815

Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?