Decentralized finance (DeFi) has emerged as a revolutionary trend within the cryptocurrency space, offering an alternative to traditional financial systems. Leveraging blockchain technology, DeFi platforms provide financial services such as lending, borrowing, and trading without relying on traditional intermediaries like banks. This article will delve into the rise of DeFi, its impact on traditional financial systems, and its potential future implications. We’ll explore how DeFi is reshaping finance, the benefits and challenges it presents, and what it means for the future of global financial markets.
The Emergence of Decentralized Finance
DeFi, short for decentralized finance, refers to a broad range of financial applications built on blockchain technology. Unlike traditional financial systems, which rely on centralized institutions such as banks and brokerages, DeFi platforms operate without intermediaries. Instead, they use smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code.
Key Components of Decentralized Finance
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Unlike traditional exchanges, DEXs allow users to trade cryptocurrencies directly with one another without the need for a central authority. Platforms like Uniswap and SushiSwap use automated market maker (AMM) protocols to facilitate trading, providing liquidity through pools funded by users.
- Lending and Borrowing Protocols: DeFi platforms like Aave and Compound enable users to lend and borrow cryptocurrencies without intermediaries. These protocols use smart contracts to automate the process, offering higher interest rates for lenders and lower rates for borrowers compared to traditional banks.
- Stablecoins: Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies pegged to the value of a fiat currency, typically the US dollar. Examples include USDC and DAI. They provide stability in the volatile crypto market and are widely used in DeFi for transactions, lending, and trading.
- Yield Farming and Staking: Yield farming involves providing liquidity to DeFi protocols in exchange for rewards, usually in the form of additional cryptocurrency tokens. Staking, on the other hand, involves locking up tokens to support the security and operations of a blockchain network, earning rewards in return.
- Insurance: DeFi insurance platforms like Nexus Mutual offer coverage for various risks within the DeFi ecosystem, such as smart contract failures and exchange hacks. This provides a layer of security for users participating in DeFi activities.

Benefits of DeFi
- Accessibility: DeFi opens up financial services to anyone with an internet connection, regardless of their location or socioeconomic status. This has the potential to bring banking services to the unbanked and underbanked populations worldwide.
- Transparency: Transactions on DeFi platforms are recorded on public blockchains, making them transparent and easily auditable. This reduces the risk of fraud and corruption.
- Lower Costs: By eliminating intermediaries, DeFi can reduce transaction fees and other costs associated with traditional financial services. Smart contracts automate processes that would typically require manual intervention, further reducing expenses.
- Innovation: The open-source nature of DeFi encourages innovation and collaboration. Developers can build on existing protocols to create new financial products and services, driving continuous improvement and growth.
Challenges and Risks
- Regulatory Uncertainty: DeFi operates in a largely unregulated space, leading to uncertainty and potential legal challenges. Governments and regulatory bodies are still grappling with how to oversee and integrate DeFi into the existing financial framework.
- Security Risks: DeFi platforms are vulnerable to hacks and exploits, as seen in several high-profile incidents. The reliance on smart contracts, which can have vulnerabilities, poses significant risks to users’ funds.
- Scalability: As DeFi grows, the underlying blockchain networks, particularly Ethereum, face scalability issues. High transaction fees and slow processing times can hinder the user experience and limit the growth potential of DeFi platforms.
- Complexity: The technical nature of DeFi can be daunting for new users. Understanding how to interact with different protocols, manage private keys, and navigate potential risks requires a level of knowledge that may not be accessible to everyone.
The Future of DeFi
The future of DeFi holds immense potential, but it will depend on addressing the challenges and risks currently facing the ecosystem. Here are some potential developments to watch for:
- Regulatory Clarity: As governments and regulatory bodies gain a better understanding of DeFi, clearer regulations will emerge. This could provide a more secure environment for users and encourage wider adoption.
- Interoperability: Efforts to enhance interoperability between different blockchain networks are underway. Projects like Polkadot and Cosmos aim to create a more interconnected and scalable DeFi ecosystem, enabling seamless communication and transactions across various platforms.
- Institutional Involvement: As DeFi matures, institutional investors are likely to take a greater interest. This could bring more liquidity and stability to the market, while also driving innovation and development.
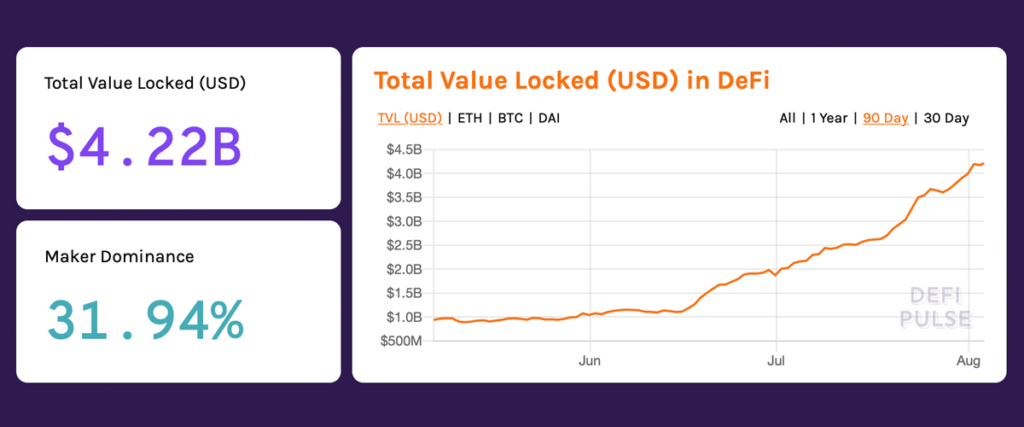
From the Past to the Future
The DeFi movement began gaining traction around 2018, with Ethereum being the primary blockchain supporting DeFi applications due to its robust smart contract capabilities. Over the past few years, DeFi has grown exponentially. As of mid-2020, the total value locked (TVL) in DeFi protocols had surpassed $150 billion, up from just $1 billion in 2019. This rapid growth highlights the increasing interest and investment in decentralized financial services.
Visits: 10025

